RAG In Production - Best Practices Notes
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) method are transforming the landscape of natural language processing by combining the strengths of retrieval-based and generative models (LLMs). When deployed in production, RAG systems can provide more accurate and contextually relevant responses. This guide outlines best practices for implementing RAG models in a production environment, ensuring robustness, scalability, and efficiency.
Why RAG?
The exact question is: Why using RAG instead of only LLM models? Consider the two-main reasons:
-
Reduce hallucination: RAG can provide more accurate and contextually relevant responses by combining the strengths of retrieval-based and generative models.
-
External knowledge / Up-to-date information: With In-Context Learning, we can added new knowledge to the model without retraining the model.
Well, but fine-tuning a LLM model can also adding the external knowledge to the model, then improve the model's performance. So, the question is: When should we use RAG instead of fine-tuning a LLM model?
Take a look at the following comparison:
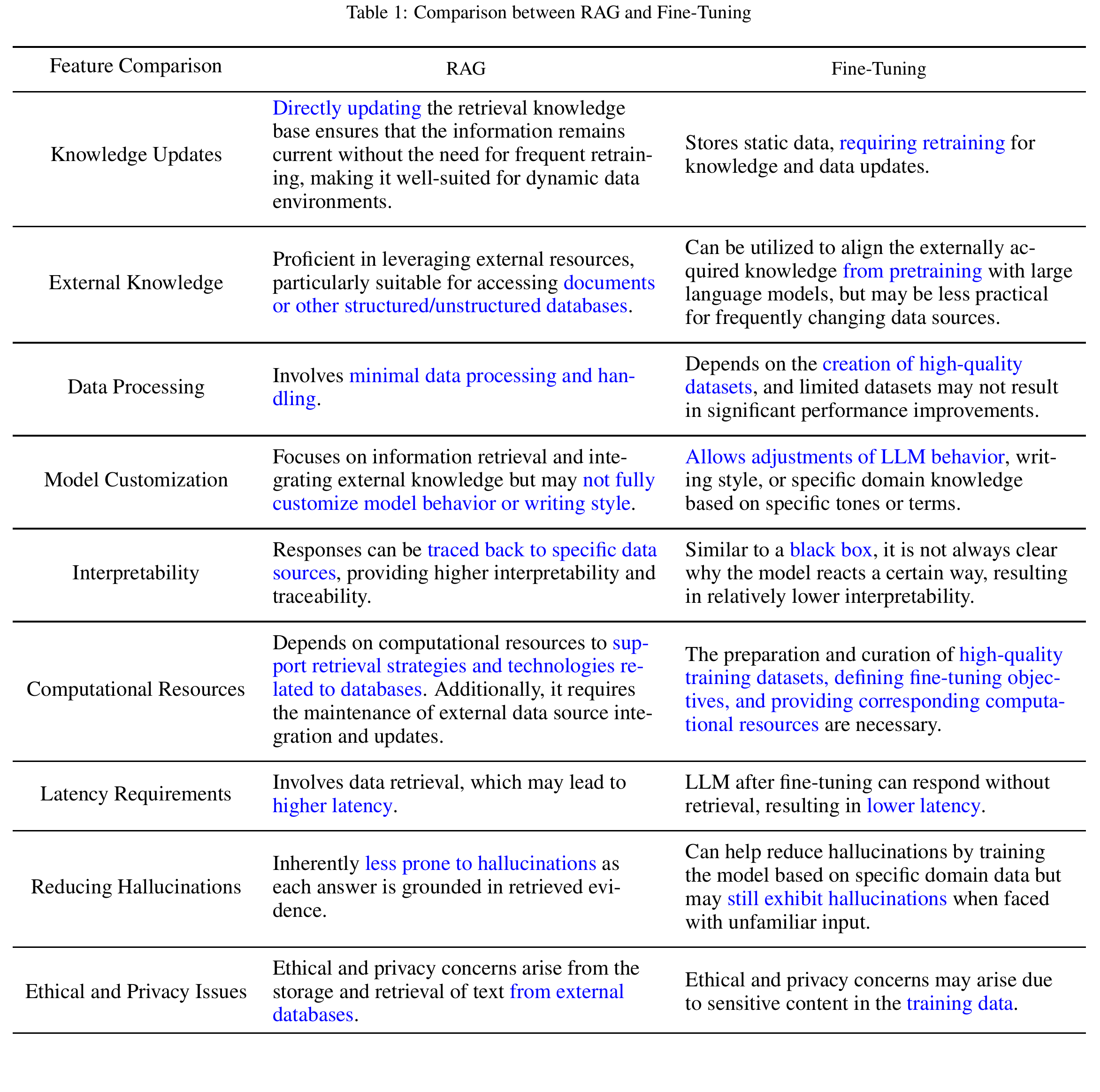
Comparison between RAG and Fine-tuning, source: Tongji-KGLLM/RAG-Survey
Both of RAG and fine-tuning have their own pros and cons. But if you can accept the cons of RAG, then RAG is more suitable for the following cases:
- When the external knowledge is dynamic and frequently updated.
- Hallucination: RAG can provide more accurate and contextually relevant responses.
- Controlability: RAG can provide more control over the generation process.
The above comparison is not correct with OpenAI fine-tuning mechanism. It is not good for adding external knowledge to the model. Please refer to the OpenAI video for more information.
RAG best practices
In this section, we will outline best practices for implementing RAG in a production environment. These practices are designed to ensure robustness, scalability, and efficiency. We will first talk about the problem of RAG, then we will provide the best practices to solve the problem.
Try the simple method first
If you are not sure which RAG method is the best for your problem, try the simple method first. A good starting method is the RAG with BM25 retrieval method. The BM25 retrieval method is simple, efficient, and effective for many problems.
BM25 algorithm is a keyword-based retrieval algorithm, some of the following tips can help you improve the performance of the BM25 algorithm:
- Remove the stop words.
- Use the stemming algorithm.
- Convert the text to lowercase.
- Extract and using the keywords from text.
- Generate variants of search queries and documents, i.e., synonyms, paraphrases, etc.
Even if the BM25 algorithm is not get the good performance, it still can consider as a baseline for the more complex RAG methods.
- You have the baseline to compare with other experiments, to know your future experiments are better or not.
- You can analyze the issues or weakness of the BM25 algorithm, then easier to find the solution for the issues.
Maintain the hierarchical structure of your documents.
The hierarchical structure of your documents is crucial for the performance of RAG models. The hierarchical structure allows the model to efficiently retrieve relevant information and generate contextually relevant responses. When designing your documents, make sure to organize them in a hierarchical manner, with clear headings and subheadings.
What is the hierarchical structure of a document?
- For a Wikipedia article, the hierarchical structure could be: Title -> Sections -> Subsections -> Paragraphs.
- For PDF documents, the hierarchical structure could be: Title -> Chapters -> Sections -> Subsections.
For example, if you just extract the text from the PDF without maintaining the hierarchical structure, then every word in the document will be treated equally.
## BUSINESS STRATEGIES
- Enhancement of our R&D capabilities to ride on trends and business opportunities arising from the digitalisation of the telecommunications industry;
- Expansion of our product range, which includes the continual development and launch of eco-friendly and ESG products such as “green and innovative antenna and subsystem solution”;
- Strengthening of our sales and marketing capabilities to capture new business opportunities and expand our customer base;
- <A long list of items>
- ...
## FUTURE PLANS
...
Consider the example text above, what happend if you don't maintain the hierarchical structure of the document?
- Your chunking strategy will not work well, since we don't have enough information to make a good chunking.
- If the query is "What are the business strategies?", only the heading matches the query, but the content does not match the query, since the text not contain the relevant words. What happend if the "bussiness stratagy" section is divided into two different chunks? or the "bussiness stratagy" line is the last line of the chunk before?
- Is LLM model easy to understand a document lossing the hierarchical structure?
Final words: Maintain the hierarchical structure of your documents directly and indirectly improve the performance of the RAG model.
- Directly: It is better for LLM to understand the document.
- Indirectly: It is better for the chunking strategy, eg. chunking by section boundaries.
- Indirectly: It is better for the implement the retrieval strategy, eg. indexing the section title to represent the section.
Take a look at the chunking strategy
The chunking algorithm help to divide the document into smaller chunks, but it is also making the "break-in-the-middle" problem. The "break-in-the-middle" problem is when the relevant information is divided into two different chunks.
Chunking is the process of dividing a document into smaller chunks to improve the efficiency of the retrieval process. The chunking strategy you choose can have a significant impact on the performance of your RAG model. When designing your chunking strategy, consider the following best practices:
-
Use the hierarchical structure of your documents to guide the chunking process. For example, you can chunk the document at section boundaries, then paragraph boundaries, then sentence boundaries.
-
Experiment with different chunk sizes to find the optimal balance between granularity and efficiency. Larger chunks may contain more context, but smaller chunks may be more efficient to process.
If your chunking is for semantic search (vector similarity), make sure that your chunks are fit into the input max_length of the embedding model. Otherwise, you may lose some information when doing the embedding.
Later, you will embedding the chunks into vector space for semantic search. So, your chunking should break document into chunks where each chunk should represent only one piece of information.
Consider using text summarization for long documents
Text summarization can be used to generate concise summaries of long documents, which can improve the efficiency of the retrieval process. By summarizing long documents, you can:
- Remove unnecessary information that may distract the model.
- Retain key information help improve the retrieval process.
- Summarize help reduce the break-in-the-middle problem of the chunking process.
- Summarize can be considered as a semantic chunking, if you summarize the document into chunks.
Depending on your problem, you can use only the summary or use the summary as additional data.
Take a look at the format of (search_query, document) pairs
In most cases, the search query is a question, while documents are not question. So, the search query and the document are in different formats. This difference in format can make it difficult for the model to retrieve relevant information.
To address this issue, consider the following best practices:
-
Generate the fake_answer for the search query, then using the fake_answer as the search_query. Then both the search_query and the document are in the same format. This idea is originally from Gao et al., ACL 2023 paper, HYDE is its short name.
-
Using LLM to generate Q&A pairs from the document, or generate FAQs from the document. Then the search_query and the document are in the same format.
Personally, I prefer the second solution, because:
- Create a good fake_answer is not easy, it is require a good LLM, such as OpenAI LLMs.
- We have time at data processing, but user don't want to wait long time for the response.
Divide and conquer
Divide and conquer is a technique for solving complex problems by breaking them down into smaller, easier-to-solve subproblems. This traditional approach can apply to many problems, including RAG.
We can use this approach in both RAG backend (data processing & ingesting) and RAG frontend (user interaction with the pipeline).
For example, we can divide the document into categories, or organize the data into a hierarchy structure. This helps narrow down the retrieval scope, thus improving the accuracy of the search results.
On the other hand, we can also use this approach to divide the search query into categories - this is often call query router, which helps route the search query to the right pipeline. Another example is break the query into sub-queries.
Thats some idea to consider, feel free to explore more or modify it to match your needs.
Moving tasks from RAG-frontend to RAG-backend
Generally, the RAG model is divided into two parts:
- RAG-frontend: Where user interact with the pipeline, eg. input the search query, retrieve the relevant documents, and generate the response.
- RAG-backend: Where you prepare the data, data processing / enrichment, and indexing the data.
The RAG-frontend is the part that user interact with the pipeline, and run every time the user input the search query. So, it should be fast and efficient. The RAG-backend is the part that run only one time, can run in the background -> it can be slow.
So, think about moving the tasks from RAG-frontend to RAG-backend, if it is possible. That is why I prefer convert document to Q&A pairs in the data processing step, instead of generate the fake_answer in the RAG-frontend.
Consider the below PDF's content (A troubleshooting guide for a software product):
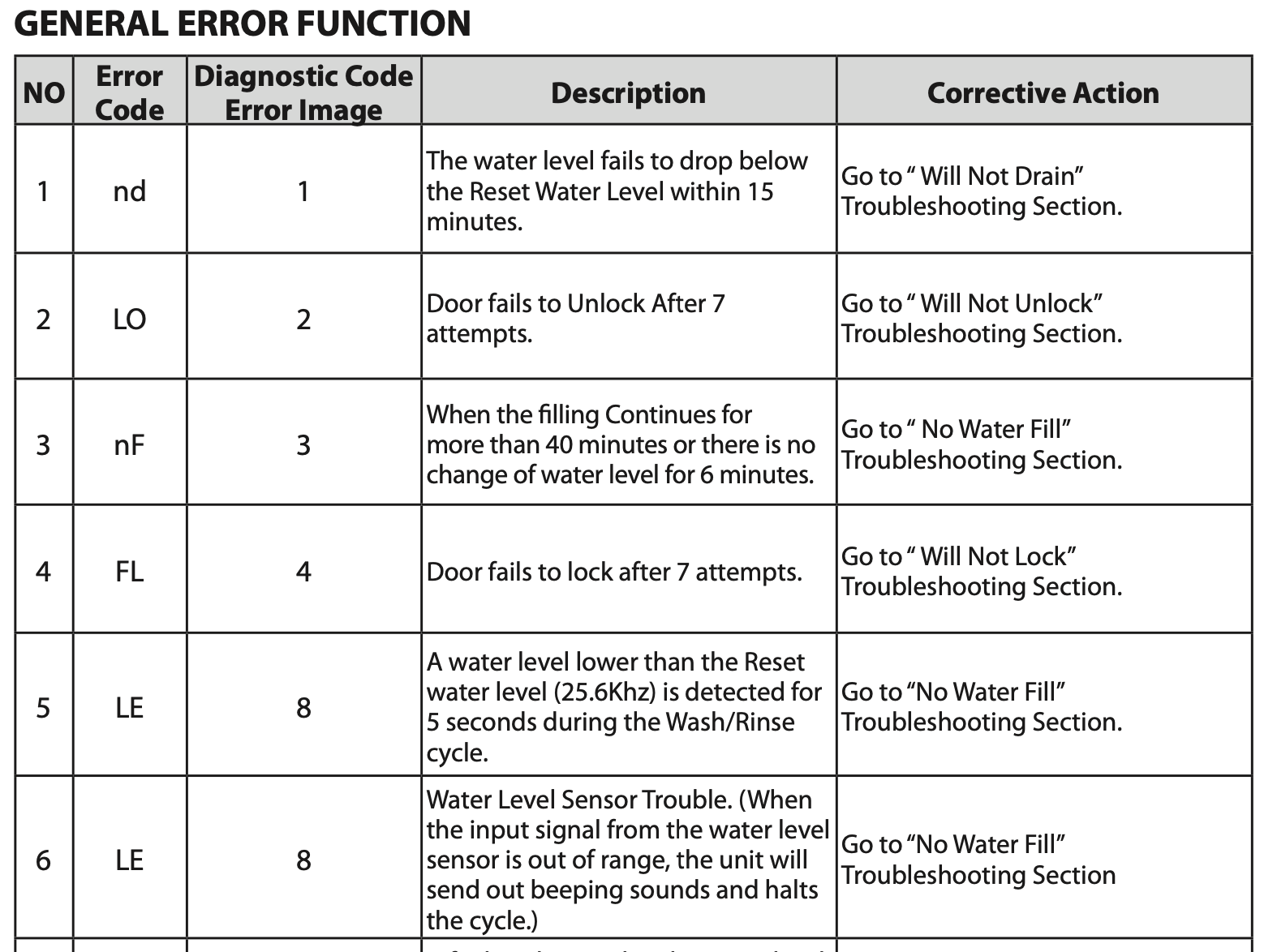
If you are using the common RAG method, you can see that your RAG won't work well with the above content with the query like: How to fix the error code XX?
The reason is the error code (keyword) in the document not directly mention the solution, it is refer the reader go to another section to find the solution.
There are some approachs such as Chain of Thought, Iteratively Search (Multi-step retrieval) can help you solve the problem. Because they are using LLM after every search to evaluate the relevance of the search result, then decide the next action.
However, these approaches are on the frontend side, which not only takes time but also costs money. In this case, you should consider moving to RAG-backend side.
Conclusion
RAG models are transforming the landscape of natural language processing by combining the strengths of retrieval-based and generative models. When deployed in a production environment, RAG systems can provide more accurate and contextually relevant responses. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can ensure the robustness, scalability, and efficiency of your RAG implementation.
In summary, the best practices for implementing RAG in a production environment include:
- Try the simple method first.
- Maintain the hierarchical structure of your documents.
- Take a look at the chunking strategy.
- Consider using text summarization for long documents.
- Take a look at the format of (search_query, document) pairs.
- Moving tasks from RAG-frontend to RAG-backend.
Thank you for reading this guide, and we hope you found it helpful. If you have any questions or would like to learn more about RAG, feel free to reach out to us.